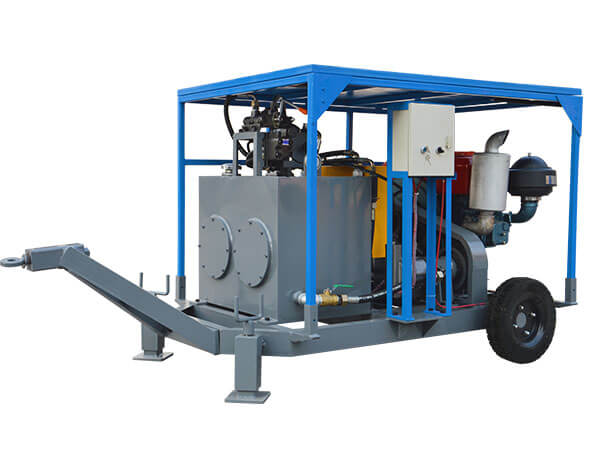
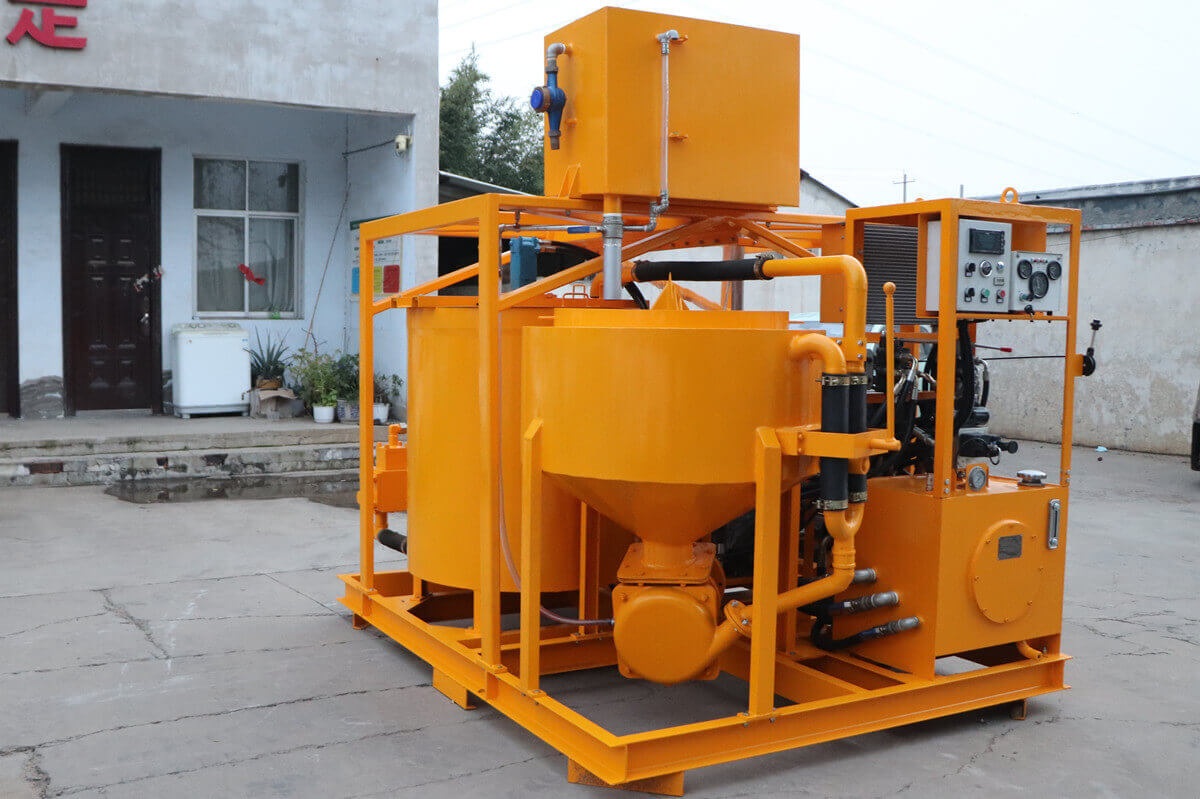
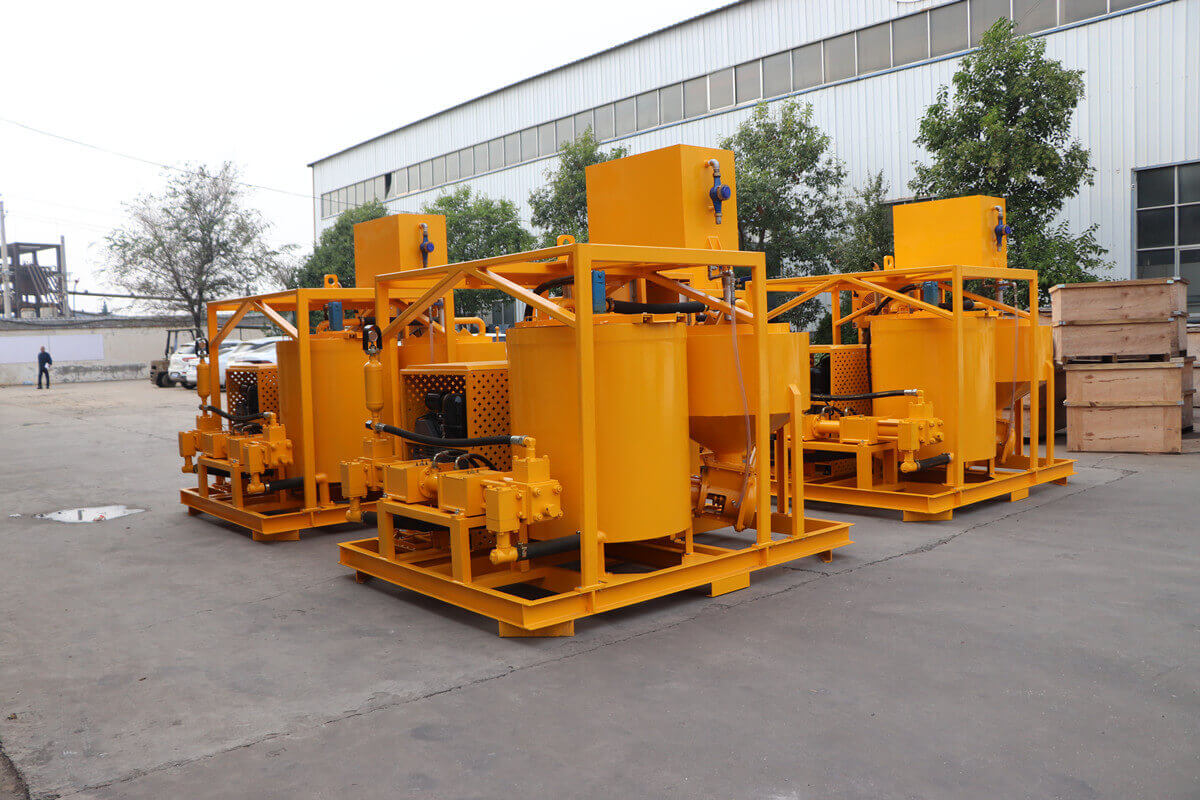
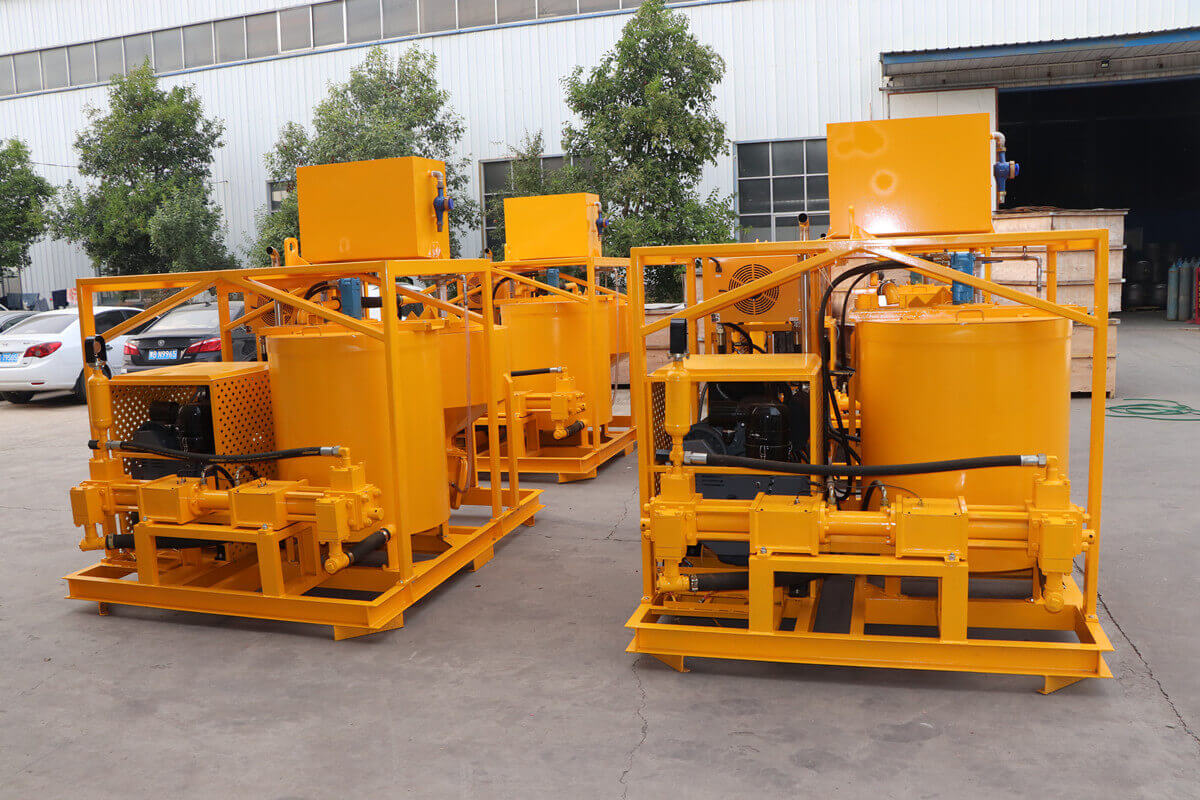
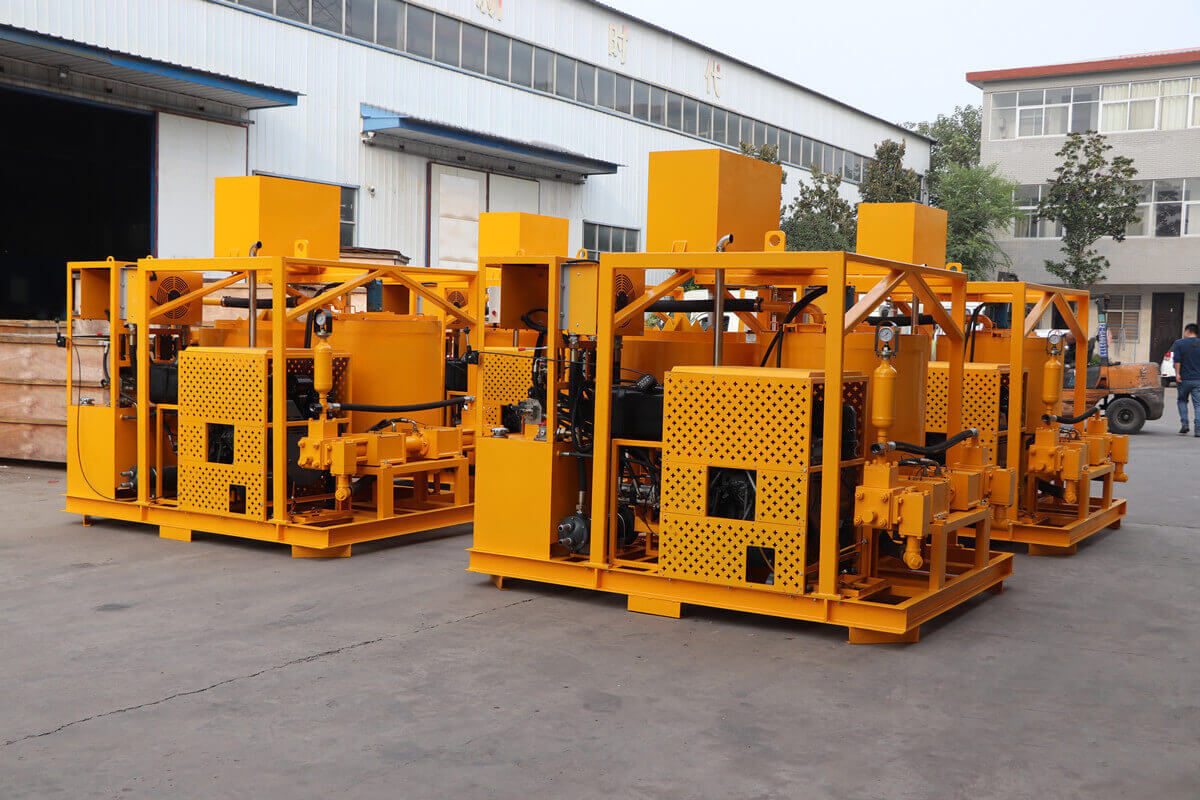
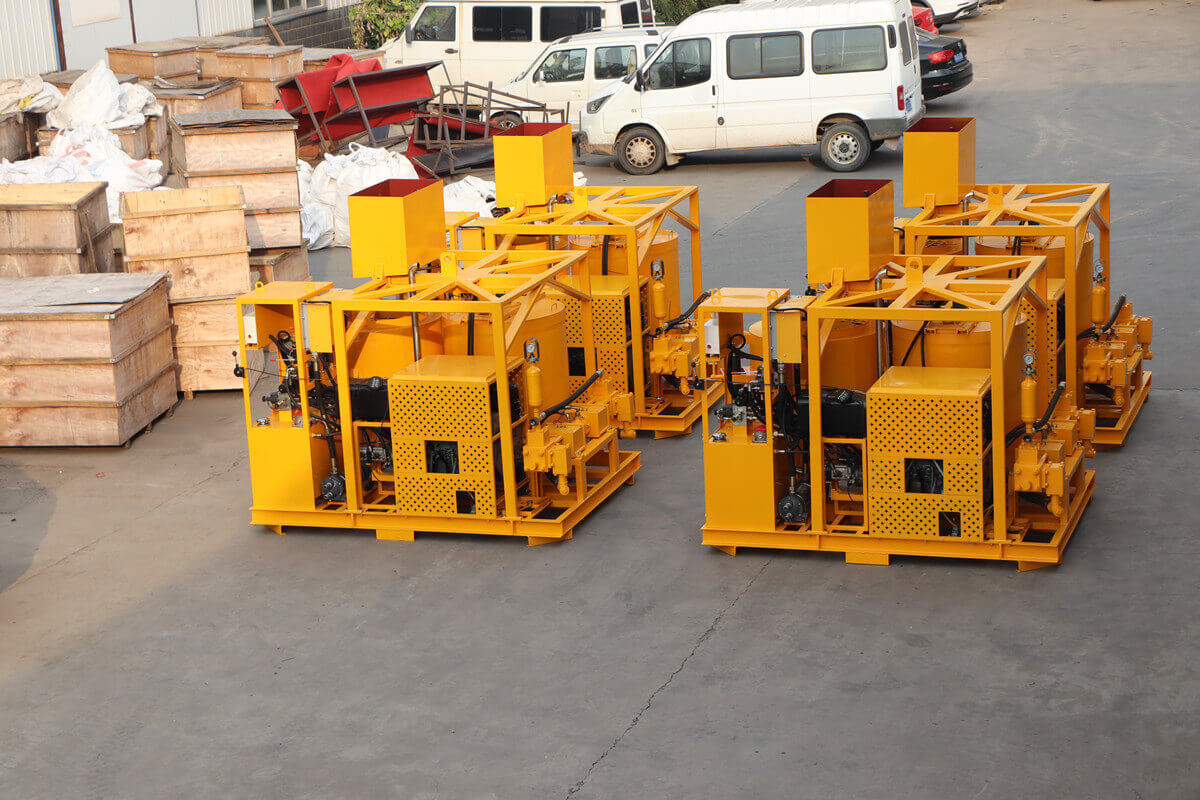
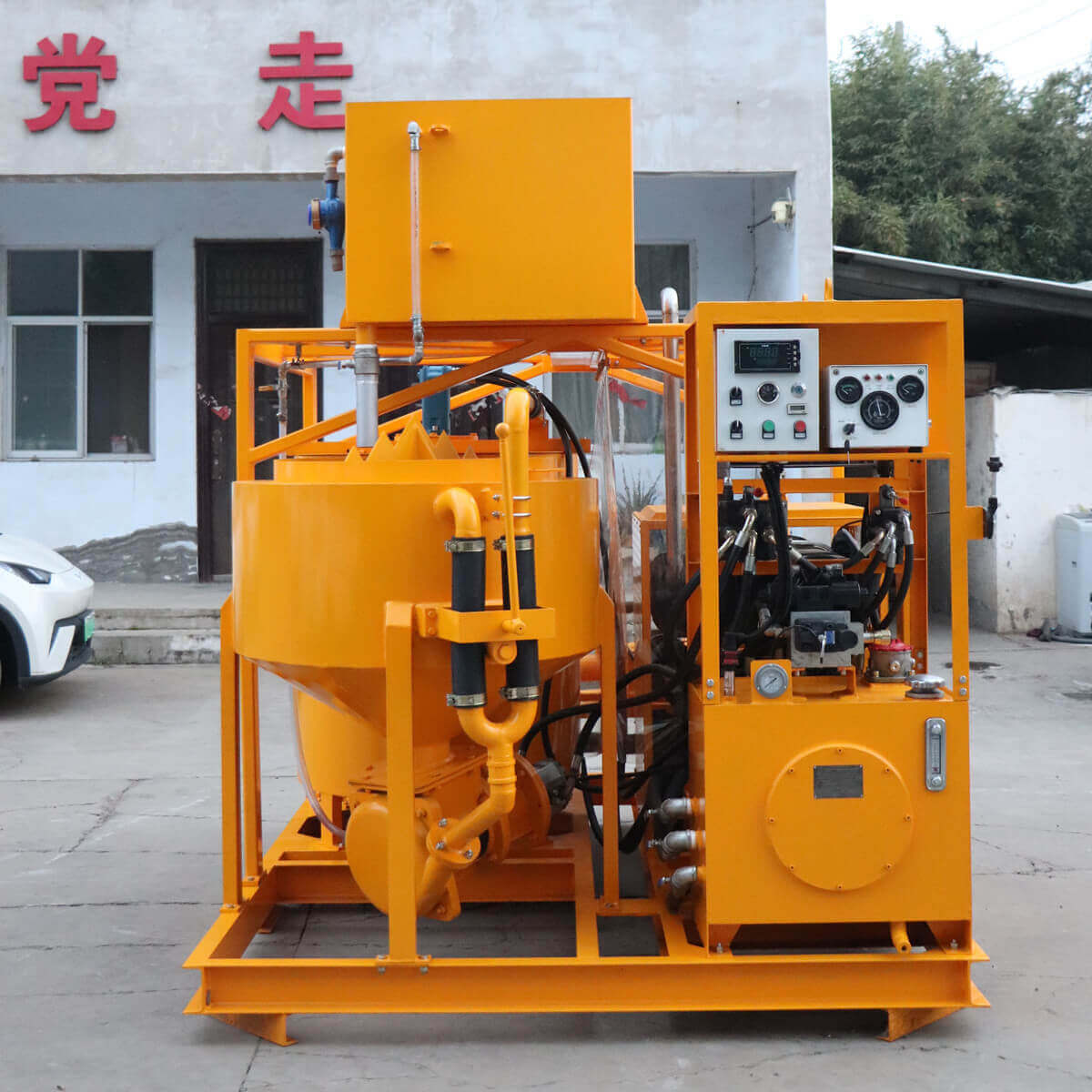
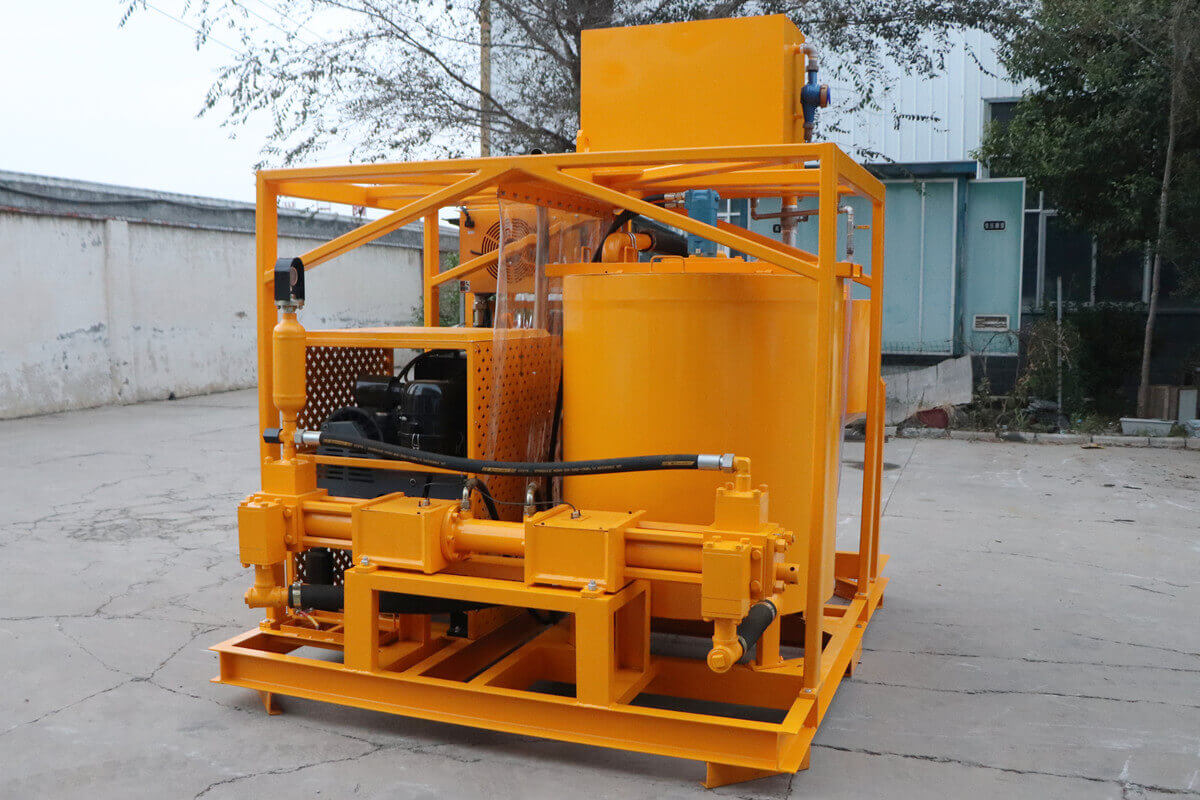
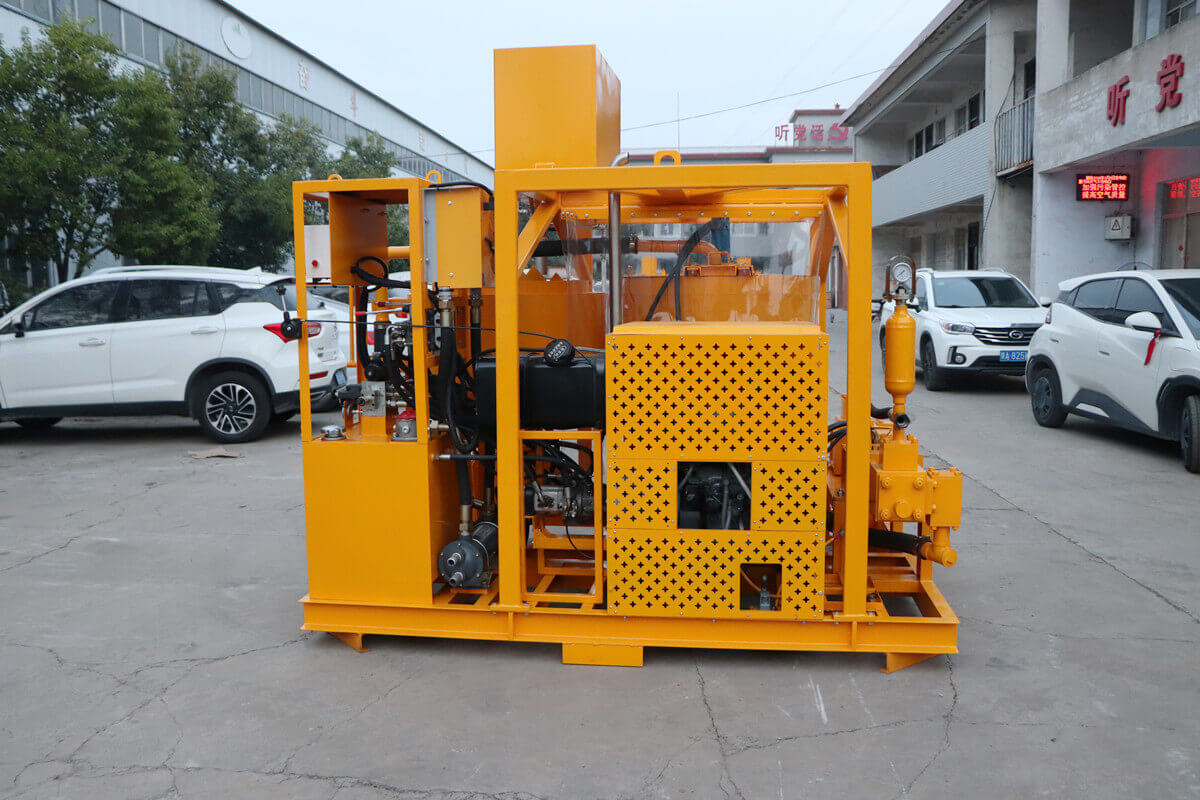
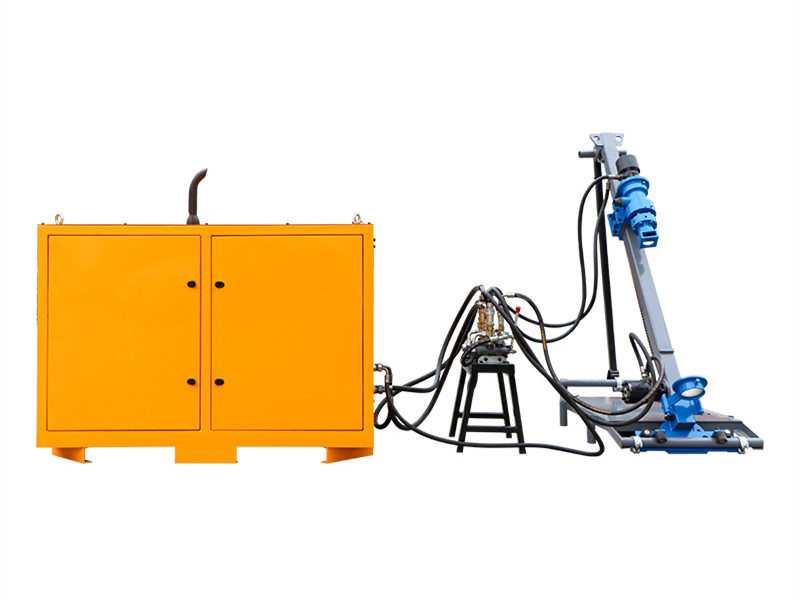
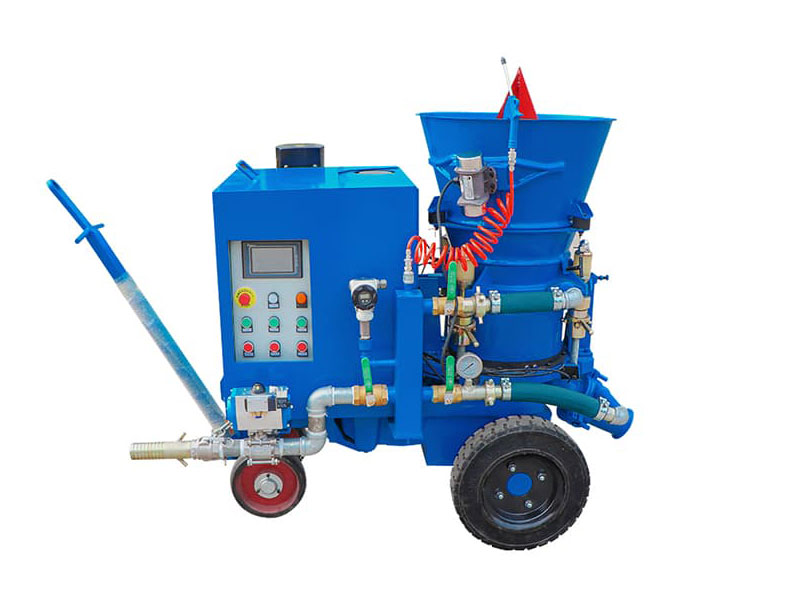
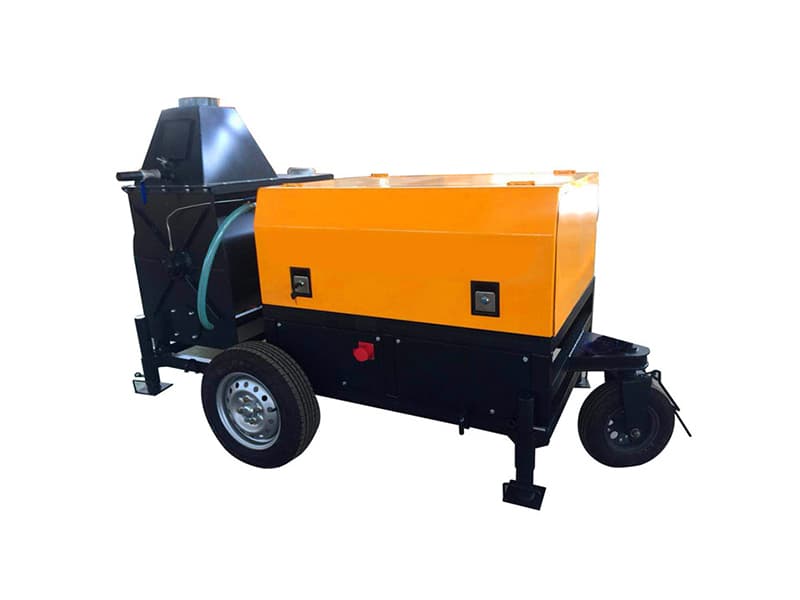
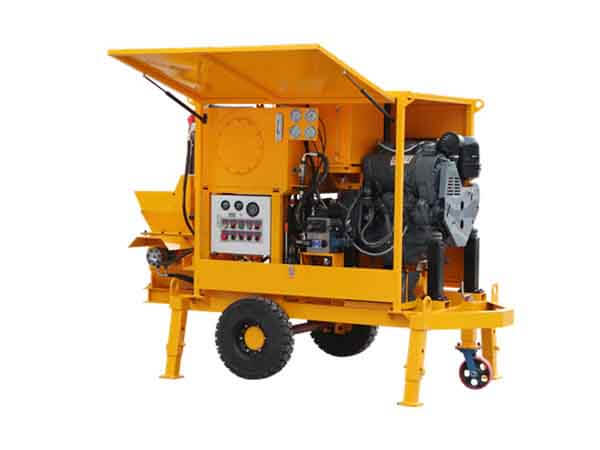
Grouting plant for ground anchor injection is a factory dedicated to the production of grouting materials, which are usually used in ground anchor grouting projects such as foundation reinforcement, tunnel support, slope stabilization, etc. in civil engineering. Ground anchor grouting, as one of the applications, has specific requirements for the quality and performance of grouting materials.
Commonly used grouting materials include cement grout, bentonite grout and chemical grout. The selection of these materials should be based on the specific requirements of the project, geological conditions, grouting pressure and curing time. Grouting materials should have good fluidity, stability and strength to ensure that they can fully penetrate into the pores of soil or rock during the grouting process and form good bonding with the anchor.
Ground anchor injection significantly enhances the stability of structures by providing additional support. It can be a more cost-effective solution compared to traditional foundation methods, especially in difficult or sensitive ground conditions. The process is relatively non-invasive and can be carried out with minimal disruption to the surrounding area.
Process of ground anchor injection:
1. Site Preparation: Before grouting, the site must be prepared by drilling holes to the required depth and installing the ground anchors.
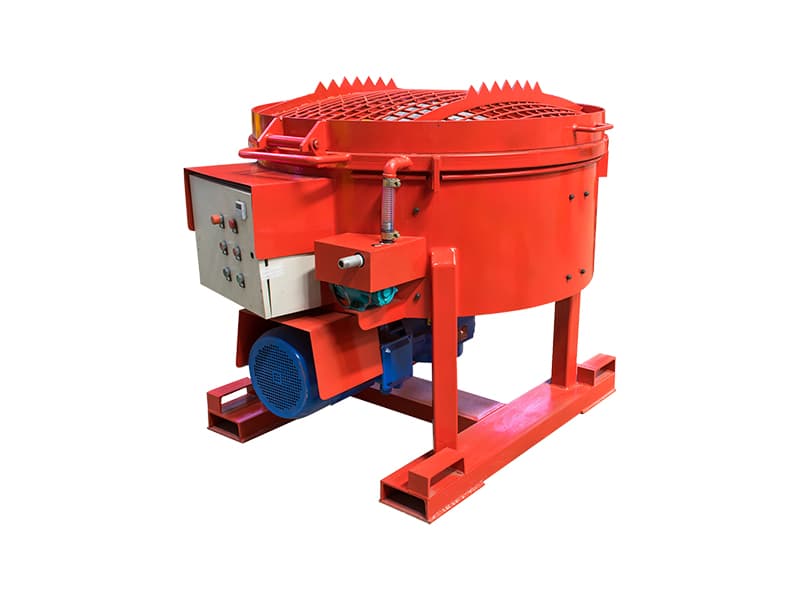
2. Grout Preparation: The grout is mixed according to the specific requirements of the project, which may vary depending on the soil conditions and the type of structure being stabilized.
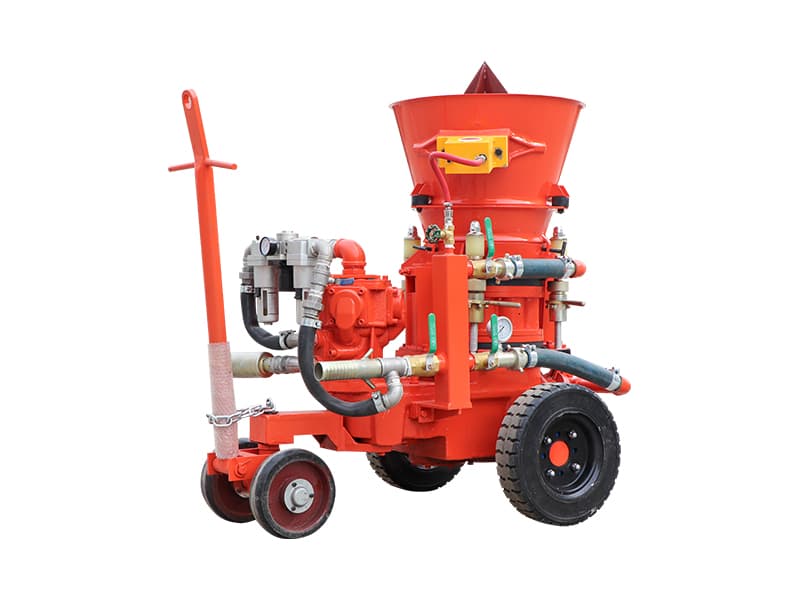
3. Injection: The grout is pumped into the boreholes under high pressure. The pressure is carefully controlled to ensure that the grout fills the voids around the anchor and bonds with the surrounding soil or rock.
4. Monitoring: During the injection process, the grouting plant's control system monitors the pressure and flow rate to ensure that the grout is being distributed evenly and effectively.
5. Curing: After injection, the grout needs time to cure and harden. This process can take several hours to days, depending on the type of grout and environmental conditions.
6. Testing: Once the grout has cured, the anchors are tested to ensure they have achieved the required load-bearing capacity.
Grouting plant for ground anchor injection can also be widely used in construction, engineering and mining industries. Application areas:
Anchor Injection:
Used for stabilizing soil and rock formations, especially in slope stabilization, retaining walls, and underground structures.
Anchors are injected into the ground to provide tensile strength and prevent movement.
Grouting:
Applied to fill voids, cracks, and gaps in concrete, masonry, and soil structures.
Enhances the structural integrity and load-bearing capacity of the structure.
Cavity Filling:
Used to fill empty spaces or voids in underground tunnels, mines, and other excavations.
Helps prevent collapse and stabilize the surrounding rock or soil.
Micro Tunnelling:
A trenchless method of installing pipelines and other underground utilities.
Involves using a small-diameter tunneling machine to create a bore, which is then lined with a pipe or other material.
Ground Injection:
Involves injecting materials into the ground to stabilize it, improve its bearing capacity, or control groundwater flow.
Commonly used in foundation engineering, slope stabilization, and underground construction.
Bentonite Lubrication:
Bentonite is used as a lubricant in drilling and tunneling operations.
It reduces friction between the drilling tool and the surrounding rock or soil, making the operation more efficient and reducing wear and tear on equipment.
Mixing of grouting materials:
Cement Slurries:
Mixtures of cement, water, and sometimes other additives are used in grouting and underground construction.
Provide strength and stability to the surrounding soil or rock.
Anchor Grout:
A specialized type of grout is used in anchor injection.
It has high compressive strength and bond strength to ensure the anchor is securely fixed in place.
Bentonite Slurries:
Mixtures of bentonite clay and water are used in drilling, tunneling, and grouting operations.
Bentonite's swelling properties make it an effective sealing and lubricating agent.
Filling Material for Peripheral Sealing:
Materials used to seal the perimeter of underground structures, such as tunnels and shafts.
Commonly includes grout, cement slurries, or other materials that can be injected or pumped into place.
Insulation Slurries:
Mixtures are used to provide thermal insulation in underground structures.
Often contains specialized materials that have high thermal resistance and can be injected or sprayed into place.
Fly Ash Slurries:
Mixtures of fly ash, water, and sometimes other additives are used in various construction and engineering applications.
Fly ash is a by-product of coal combustion and can be used as a substitute for cement in some grouting and concrete applications.
Overall, these materials and techniques play a crucial role in ensuring underground structures' stability and safety and improving the efficiency of construction and mining operations. If you have any interest in our grouting plant for ground anchor, please contact us by email, email address: sales1@leadcrete.com
Your position:
Home > News > Product News
Grouting plant for ground anchor injection
date: 2024-11-23
Inquiry
Please feel free to submit your inquiry information to us. We will contact with you as soon as possible.


.jpg)









.jpg)